Menu
Menu

Chromosome conformation capture (3C), also known as proximity-ligation, is a molecular biology approach designed to analyze the spatial organization of chromatin. When the ligation events are tagged with biotin and isolated with streptavidin subjected to paired-end whole genome sequencing it is known as Hi-C.
For further information, check out this review paper by Davis et al. (2017).
The Dovetail proximity-ligation kits are user friendly and designed for novice Hi-C users. Plus, our world-class support team is also available to help out if you run into difficulties or have questions.
They are novel Hi-C assays available only from Dovetail Genomics® and differ from traditional Hi-C in the following important ways:
Don’t see your question? Submit it to our support team: support@cantatabio.com
The Dovetail HiChIP MNase assay leverages the Micro-C (MNase-based Hi-C) workflow to conduct chromatin digestions. With the HiChIP MNase assay:
Inclusion of ChIP-seq data simplifies data QC and interpretation but is not an absolute requirement. You can use publicly available data from sources such as ENCODE if you have not generated ChIP-seq data. However, it will not be truly reflective of your experiment or sample of interest.
This will vary depending on the antibody/protein of interest. See table below.
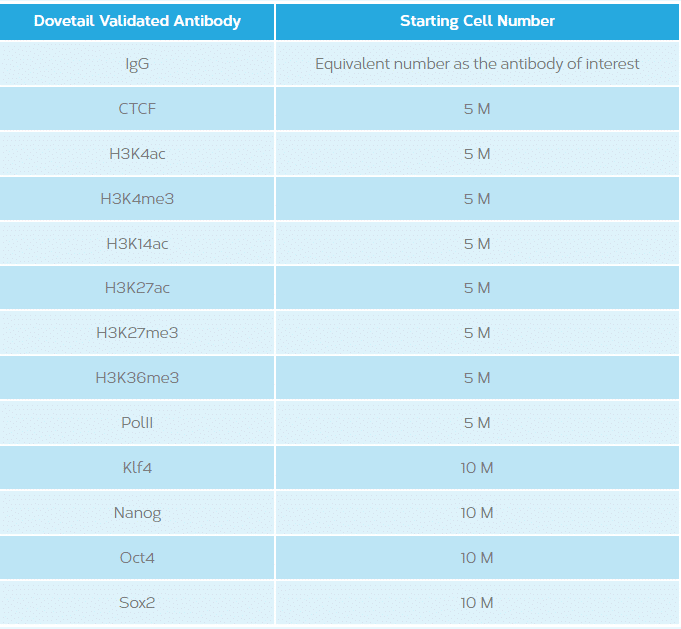
This will vary depending on the occurrence rate of protein-DNA interactions of the protein of interest and the genome in question. The following are recommended starting guidelines:
Dovetail has compiled a comprehensive best practices step-by-step workflow with full documentation that covers:
The Dovetail HiChIP QC tool that assesses the success of a Dovetail HiChIP library requires the raw HiChIP sequence data (*.fq.gz), a reference genome (*.fa) and a file of 1D ChIP-seq peak locations (*.bed).
Micro-C uses micrococcal nuclease (MNase) to digest chromatin instead of the restriction enzymes other Hi-C methods use. This approach provides superior signal–to–noise, enabling nucleosome resolution/nucleosome phasing and a more granular view of chromatin folding that includes enhancer-promoter/promoter-promoter interactions and loop extrusion features.
The standard input for Micro-C assay is one million cells.
You will get 8 reactions with each Micro-C kit.
It only takes 1.5 days to go from sample to sequencing-ready library!
The Micro-C workflow does not require sonication. The fragmentation is enzymatic and is carried out at Stage 1 of the protocol.
Since your experimental design will determine the types of downstream analyses available to you, it is critical to consider both in unison prior to generating any data. You can find a detailed discussion of the Micro-C experimental design here.
Micro-C libraries are Illumina compatible. We recommend sequencing 2 x 75 bp, 2 x 100 bp, or 2 x 150 bp.
Dovetail has compiled a comprehensive best practices step-by-step workflow with full documentation that covers:
Dovetail tools for QC and Contact Matrix generation require the Micro-C raw sequence data (*.fq.gz) and a reference genome assembly (*.fa).
Due to the use of restriction enzymes and sonication, traditional Hi-C valid reads require the insert size (or physical coverage) of a read-pair to be greater than the library fragment and to be adjacent to a restriction site. Micro-C libraries do not use restriction enzymes or require sonication (a key source of noise in Hi-C libraries). Therefore, a valid Micro-C read only requires that the insert size (or physical coverage) of a read-pair be greater than the library fragment. Check out this white paper to learn more.
The standard input for Omni-C is one million cells. A low input protocol is also supported down to one thousand cells.
Cells, animal and plant tissues, and blood.
You will get 8 reactions with each Omni-C kit.
The workflow from sample to sequencing–ready library is split over two days.
The Omni-C kit is compatible with hybrid capture approaches. The Omni-C workflow integrates easily with Agilent SureSelect, Illumina TruSight and IDT xGEN.
Omni-C libraries exhibit WGS-like coverage of the genome and do not use restriction enzymes; therefore, you can use off-the-shelf probe sets or design your own probes without an inclusion of a restriction enzyme site.
Yes, frozen cells previously cross-linked with formaldehyde concentration ≥ 1% can be used as input to the assay. Simply skip the formaldehyde fixation step of our recommended two step fixation process.
Dovetail offers library preparation and index primers modules to streamline the library preparation workflow. Omni-C is compatible with third party library preparation kits as well, namely NEBNext® Ultra™ II DNA Library Prep Kit for Illumina®, Kapa® HyperPrep, and Swift Biosciences Accel-NGS® 2S Plus DNA Library Kit.
The Omni-C workflow does not require sonication. The fragmentation is enzymatic and is carried out at Stage 1 of the protocol.
Omni-C libraries are Illumina compatible. We recommend sequencing 2 x 150 bp. One library is typically sufficient for the generation of ~300M total read-pairs. Depending upon final sequencing depth desired, multiple libraries may need to be pooled prior to the sequencing run.
Dovetail has compiled a comprehensive best practices step-by-step workflow with full documentation that covers:
Dovetail tools for QC and Contact Matrix generation require the Omni-C raw sequence data (*.fq.gz) and a draft assembly (genome *.fa).
Due to the use of restriction enzymes and sonication, traditional Hi-C valid reads require the insert size (or physical coverage) of a read-pair to be greater than the library fragment and to be adjacent to a restriction site. Micro-C libraries do not use restriction enzymes or require sonication (a key source of noise in Hi-C libraries). Therefore, a valid Micro-C read only requires that the insert size (or physical coverage) of a read-pair be greater than the library fragment as defined by HiC-Pro. Check out this white paper to learn more.
HiC-Pro is also compatible with Omni-C libraries. Note that there are custom configuration files that are required. Please reach out to us at Dovetail for guidance on how to run HiC-Pro.
This largely depends on application. The following recommendations are good starting points: